string1 <- "This is a string"
string2 <- 'If I want to include a "quote" inside a string, I use single quotes'Pre-lecture materials
Read ahead
Before class, you can prepare by reading the following materials:
Acknowledgements
Material for this lecture was borrowed and adopted from
Learning objectives
At the end of this lesson you will:
- Understand what is a ‘regular expression’ and how to create one
- Learn the basics of searching for patterns in character strings in base R and the
stringrR package in thetidyverse - Use the built in character sets to search for patterns in strings including
"\n","\t","\w","\d", and"\s"
Introduction
regex basics
A regular expression (also known as a “regex” or “regexp”) is a concise language for describing patterns in character strings.
Regex could be patterns that could be contained within another string.
For example, if we wanted to search for the pattern “ai” in the character string “The rain in Spain”, we see it appears twice!
“The rain in Spain”
Generally, a regular expression can be used for e.g.
- searching for a pattern or string within another string (e.g searching for the string “a” in the string “Maryland”)
- replacing one part of a string with another string (e.g replacing the string “t” with “p” in the string “hot” where you are changing the string “hot” to “hop”)
If you have never worked with regular expressions, it can seem like maybe a baby hit the keys on your keyboard (complete gibberish), but it will slowly make sense once you learn the syntax.
Soon you will be able create incredibly powerful regular expressions in your day-to-day work.
string basics
In R, you can create (character) strings with either single quotes ('hello!') or double quotes ("hello!") – no difference (not true for other languages!).
I recommend using the double quotes, unless you want to create a string with multiple ".
Strings can be tricky when executing them. If you forget to close a quote, you’ll see +
> "This is a string without a closing quote
+
+
+ HELP I'M STUCKIf this happen to you, take a deep breath, press Escape and try again.
Multiple strings are often stored in a character vector, which you can create with c():
c("one", "two", "three")[1] "one" "two" "three"grepl()
One of the most basic functions in R that uses regular expressions is the grepl(pattern, x) function, which takes two arguments and returns a logical:
- A regular expression (
pattern) - A string to be searched (
x)
In case you are curious, “grepl” literally translates to “grep logical”.
If the string (x) contains the specified regular expression (pattern), then grepl() will return TRUE, otherwise it will return FALSE.
Let’s take a look at one example:
regular_expression <- "a"
string_to_search <- "Maryland"
grepl(pattern = regular_expression, x = string_to_search)[1] TRUEIn the example above, we specify the regular expression "a" and store it in a variable called regular_expression.
Remember that regular expressions are just strings!
We also store the string "Maryland" in a variable called string_to_search.
The regular expression "a" represents a single occurrence of the character "a". Since "a" is contained within "Maryland", grepl() returns the value TRUE.
Let’s try another simple example:
regular_expression <- "u"
string_to_search <- "Maryland"
grepl(pattern = regular_expression, x = string_to_search)[1] FALSEThe regular expression "u" represents a single occurrence of the character "u", which is not a sub-string of "Maryland", therefore grepl() returns the value FALSE.
Regular expressions can be much longer than single characters. You could for example search for smaller strings inside of a larger string:
grepl("land", "Maryland")[1] TRUEgrepl("ryla", "Maryland")[1] TRUEgrepl("Marly", "Maryland")[1] FALSEgrepl("dany", "Maryland")[1] FALSESince "land" and "ryla" are sub-strings of "Maryland", grepl() returns TRUE, however when a regular expression like "Marly" or "dany" is searched grepl() returns FALSE because neither are sub-strings of "Maryland".
state.name
There is a dataset that comes with R called state.name which is a vector of strings, one for each state in the United States of America.
We are going to use this vector in several of the following examples.
head(state.name)[1] "Alabama" "Alaska" "Arizona" "Arkansas" "California"
[6] "Colorado" length(state.name)[1] 50Next, we will build a regular expression for identifying several strings in this vector of character strings, specifically a regular expression that will match names of states that both start and end with a vowel.
The state name could start and end with any vowel, so we will not be able to match exact sub-strings like in the previous examples. Thankfully we can use metacharacters to look for vowels and other parts of strings.
metacharacters
The first metacharacter that we will discuss is ".".
The metacharacter that only consists of a period represents any character other than a new line (we will discuss new lines soon).
Let’s take a look at some examples using the period regex:
grepl(".", "Maryland")[1] TRUEgrepl(".", "*&2[0+,%<@#~|}")[1] TRUEgrepl(".", "")[1] FALSEAs you can see the period metacharacter is very liberal.
This metacharacter is most useful when you do not care about a set of characters in a regular expression.
Here is another example
grepl("a.b", c("aaa", "aab", "abb", "acadb"))[1] FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUEIn the case above, grepl() returns TRUE for all strings that contain an a followed by any other character followed by a b.
repetition
You can specify a regular expression that contains a certain number of characters or metacharacters using the enumeration metacharacters (or sometimes called quantifiers).
+: indicates that one or more of the preceding expression should be present (or matches at least 1 time)*: indicates that zero or more of the preceding expression is present (or matches at least 0 times)?: indicates that zero or 1 of the preceding expression is not present or present at most 1 time (or matches between 0 and 1 times)
Let’s take a look at some examples using these metacharacters:
# Does "Maryland" contain one or more of "a" ?
grepl("a+", "Maryland")[1] TRUE# Does "Maryland" contain one or more of "x" ?
grepl("x+", "Maryland")[1] FALSE# Does "Maryland" contain zero or more of "x" ?
grepl("x*", "Maryland")[1] TRUEIf you want to do more than one character, you need to wrap it in ().
# Does "Maryland" contain zero or more of "x" ?
grepl("(xx)*", "Maryland")[1] TRUELet’s practice a few out together. Make the following regular expressions for the character string “spookyhalloween”:
- Does “zz” appear 1 or more times?
- Does “ee” appear 1 or more times?
- Does “oo” appear 0 or more times?
- Does “ii” appear 0 or more times?
## try it outYou can also specify exact numbers of expressions using curly brackets {}.
{n}: exactly n{n,}: n or more{,m}: at most m{n,m}: between n and m
For example "a{5}" specifies “a exactly five times”, "a{2,5}" specifies “a between 2 and 5 times,” and "a{2,}" specifies “a at least 2 times.” Let’s take a look at some examples:
# Does "Mississippi" contain exactly 2 adjacent "s" ?
grepl("s{2}", "Mississippi")[1] TRUE# This is equivalent to the expression above:
grepl("ss", "Mississippi")[1] TRUE# Does "Mississippi" contain between 1 and 3 adjacent "s" ?
grepl("s{1,3}", "Mississippi")[1] TRUE# Does "Mississippi" contain between 2 and 3 adjacent "i" ?
grepl("i{2,3}", "Mississippi")[1] FALSE# Does "Mississippi" contain between 2 adjacent "iss" ?
grepl("(iss){2}", "Mississippi")[1] TRUE# Does "Mississippi" contain between 2 adjacent "ss" ?
grepl("(ss){2}", "Mississippi")[1] FALSE# Does "Mississippi" contain the pattern of an "i" followed by
# 2 of any character, with that pattern repeated three times adjacently?
grepl("(i.{2}){3}", "Mississippi")[1] TRUELet’s practice a few out together. Make the following regular expressions for the character string “spookyspookyhalloweenspookyspookyhalloween”:
- Search for “spooky” exactly 2 times. What about 3 times?
- Search for “spooky” exactly 2 times followed by any character of length 9 (i.e. “halloween”).
- Same search as above, but search for that twice in a row.
- Same search as above, but search for that three times in a row.
## try it outcapture group
In the examples above, I used parentheses () to create a capturing group. A capturing group allows you to use quantifiers on other regular expressions.
In the “Mississippi” example, I first created the regex "i.{2}" which matches i followed by any two characters (“iss” or “ipp”). Then, I used a capture group to wrap that regex, and to specify exactly three adjacent occurrences of that regex.
You can specify sets of characters (or character sets or character classes) with regular expressions, some of which come built in, but you can build your own character sets too.
More on character sets next.
character sets
First, we will discuss the built in character sets:
- words (
"\\w") = Words specify any letter, digit, or a underscore - digits (
"\\d") = Digits specify the digits 0 through 9 - whitespace characters (
"\\s") = Whitespace specifies line breaks, tabs, or spaces
Each of these character sets have their own compliments:
- not words (
"\\W") - not digits (
"\\D") - not whitespace characters (
"\\S")
Each specifies all of the characters not included in their corresponding character sets.
Technically, you are using the a character set "\d" or "\s" (with only one black slash), but because you are using this character set in a string, you need the second \ to escape the string. So you will type "\\d" or "\\s".
"\\d"[1] "\\d"So for example, to include a literal single or double quote in a string you can use \ to “escape” the string and being able to include a single or double quote:
double_quote <- "\""
double_quote[1] "\""single_quote <- '\''
single_quote[1] "'"That means if you want to include a literal backslash, you will need to double it up: "\\".
In fact, putting two backslashes before any punctuation mark that is also a metacharacter indicates that you are looking for the symbol and not the metacharacter meaning.
For example "\\." indicates you are trying to match a period in a string. Let’s take a look at a few examples:
grepl("\\+", "tragedy + time = humor")[1] TRUEgrepl("\\.", "https://publichealth.jhu.edu")[1] TRUEThe printed representation of a string is not the same as string itself, because the printed representation shows the escapes. To see the raw contents of the string, use writeLines():
x <- c("\'", "\"", "\\")
x[1] "'" "\"" "\\"writeLines(x)'
"
\There are a handful of other special characters. The most common are
"\n": newline"\t": tab,
but you can see the complete list by requesting help (run the following in the console and a help file will appear:
?"'"You will also sometimes see strings like “0b5”, this is a way of writing non-English characters that works on all platforms:
x <- c("\\t", "\\n", "\u00b5")
x[1] "\\t" "\\n" "µ" writeLines(x)\t
\n
µLet’s take a look at a few examples of built in character sets: "\w", "\d", "\s".
grepl("\\w", "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789")[1] TRUEgrepl("\\d", "0123456789")[1] TRUE# "\n" is the metacharacter for a new line
# "\t" is the metacharacter for a tab
grepl("\\s", "\n\t ")[1] TRUEgrepl("\\d", "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz")[1] FALSEgrepl("\\D", "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz")[1] TRUEgrepl("\\w", "\n\t ")[1] FALSEbrackets
You can also specify specific character sets using straight brackets [].
For example a character set of just the vowels would look like: "[aeiou]".
grepl("[aeiou]", "rhythms")[1] FALSEYou can find the complement to a specific character by putting a carrot ^ after the first bracket. For example "[^aeiou]" matches all characters except the lowercase vowels.
grepl("[^aeiou]", "rhythms")[1] TRUEranges
You can also specify ranges of characters using a hyphen - inside of the brackets.
For example:
"[a-m]"matches all of the lowercase characters betweenaandm"[5-8]"matches any digit between 5 and 8 inclusive
Let’s take a look at some examples using custom character sets:
grepl("[a-m]", "xyz")[1] FALSEgrepl("[a-m]", "ABC")[1] FALSEgrepl("[a-mA-M]", "ABC")[1] TRUEbeginning and end
There are also metacharacters for matching the beginning and the end of a string which are "^" and "$" respectively.
Let’s take a look at a few examples:
grepl("^a", c("bab", "aab"))[1] FALSE TRUEgrepl("b$", c("bab", "aab"))[1] TRUE TRUEgrepl("^[ab]*$", c("bab", "aab", "abc"))[1] TRUE TRUE FALSEOR metacharacter
The last metacharacter we will discuss is the OR metacharacter ("|").
The OR metacharacter matches either the regex on the left or the regex on the right side of this character. A few examples:
grepl("a|b", c("abc", "bcd", "cde"))[1] TRUE TRUE FALSEgrepl("North|South", c("South Dakota", "North Carolina", "West Virginia"))[1] TRUE TRUE FALSEstate.name example
Finally, we have learned enough to create a regular expression that matches all state names that both begin and end with a vowel:
- We match the beginning of a string.
- We create a character set of just capitalized vowels.
- We specify one instance of that set.
- Then any number of characters until:
- A character set of just lowercase vowels.
- We specify one instance of that set.
- We match the end of a string.
start_end_vowel <- "^[AEIOU]{1}.+[aeiou]{1}$"
vowel_state_lgl <- grepl(start_end_vowel, state.name)
head(vowel_state_lgl)[1] TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSEstate.name[vowel_state_lgl][1] "Alabama" "Alaska" "Arizona" "Idaho" "Indiana" "Iowa" "Ohio"
[8] "Oklahoma"Below is a table of several important metacharacters:
| Metacharacter | Meaning |
|---|---|
| . | Any Character |
| \w | A Word |
| \W | Not a Word |
| \d | A Digit |
| \D | Not a Digit |
| \s | Whitespace |
| \S | Not Whitespace |
| [xyz] | A Set of Characters |
| [^xyz] | Negation of Set |
| [a-z] | A Range of Characters |
| ^ | Beginning of String |
| $ | End of String |
| \n | Newline |
| + | One or More of Previous |
| * | Zero or More of Previous |
| ? | Zero or One of Previous |
| | | Either the Previous or the Following |
| {5} | Exactly 5 of Previous |
| {2, 5} | Between 2 and 5 or Previous |
| {2, } | More than 2 of Previous |
Other regex in base R
So far we’ve been using grepl() to see if a regex matches a string. There are a few other built in regex functions you should be aware of.
First, we will review our workhorse of this lesson, grepl(), which stands for “grep logical.”
grepl("[Ii]", c("Hawaii", "Illinois", "Kentucky"))[1] TRUE TRUE FALSEgrep()
Then, there is old fashioned grep(pattern, x), which returns the indices of the vector that match the regex:
grep(pattern = "[Ii]", x = c("Hawaii", "Illinois", "Kentucky"))[1] 1 2sub()
The sub(pattern, replacement, x) function takes as arguments a regex, a “replacement,” and a vector of strings. This function will replace the first instance of that regex found in each string.
sub(pattern = "[Ii]", replacement = "1", x= c("Hawaii", "Illinois", "Kentucky"))[1] "Hawa1i" "1llinois" "Kentucky"gsub()
The gsub(pattern, replacement, x) function is nearly the same as sub() except it will replace every instance of the regex that is matched in each string.
gsub("[Ii]", "1", c("Hawaii", "Illinois", "Kentucky"))[1] "Hawa11" "1ll1no1s" "Kentucky"strsplit()
The strsplit(x, split) function will split up strings (split) according to the provided regex (x) .
If strsplit() is provided with a vector of strings it will return a list of string vectors.
two_s <- state.name[grep("ss", state.name)]
two_s[1] "Massachusetts" "Mississippi" "Missouri" "Tennessee" strsplit(x = two_s, split = "ss")[[1]]
[1] "Ma" "achusetts"
[[2]]
[1] "Mi" "i" "ippi"
[[3]]
[1] "Mi" "ouri"
[[4]]
[1] "Tenne" "ee" The stringr package
The stringr package, written by Hadley Wickham, is part of the Tidyverse group of R packages.
This package takes a “data first” approach to functions involving regex, so usually the string is the first argument and the regex is the second argument.
The majority of the function names in stringr begin with str_*().
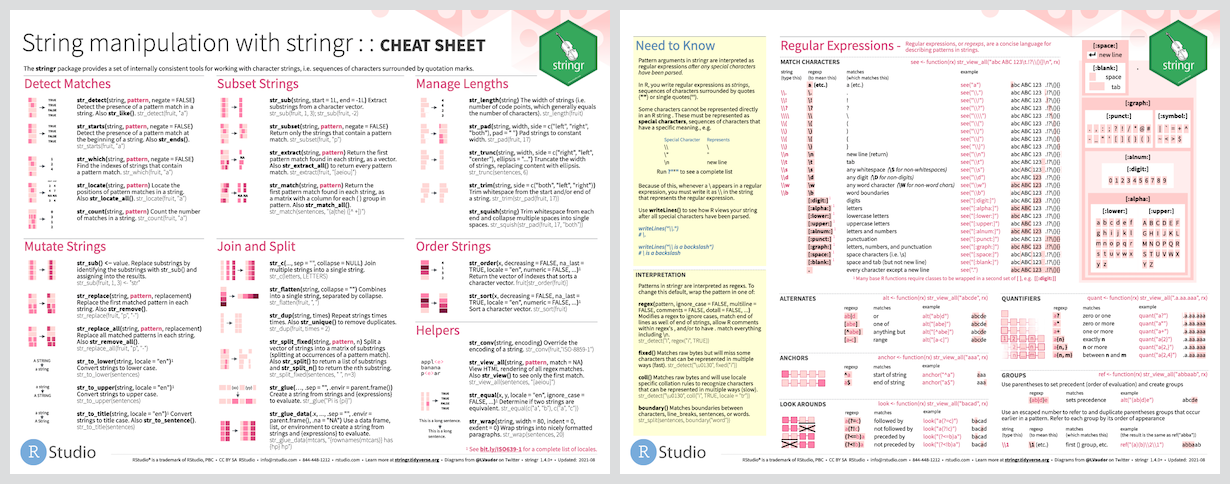
[Source: https://stringr.tidyverse.org ]
str_extract
The str_extract(string, pattern) function returns the sub-string of a string (string) that matches the provided regular expression (pattern).
library(stringr)
state_tbl <- paste(state.name, state.area, state.abb)
head(state_tbl)[1] "Alabama 51609 AL" "Alaska 589757 AK" "Arizona 113909 AZ"
[4] "Arkansas 53104 AR" "California 158693 CA" "Colorado 104247 CO" str_extract(state_tbl, "[0-9]+") [1] "51609" "589757" "113909" "53104" "158693" "104247" "5009" "2057"
[9] "58560" "58876" "6450" "83557" "56400" "36291" "56290" "82264"
[17] "40395" "48523" "33215" "10577" "8257" "58216" "84068" "47716"
[25] "69686" "147138" "77227" "110540" "9304" "7836" "121666" "49576"
[33] "52586" "70665" "41222" "69919" "96981" "45333" "1214" "31055"
[41] "77047" "42244" "267339" "84916" "9609" "40815" "68192" "24181"
[49] "56154" "97914" str_detect
The str_detect(string, pattern) is equivalent to grepl(pattern,x):
str_detect(state_tbl, "[0-9]+") [1] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
[16] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
[31] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
[46] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUEgrepl("[0-9]+", state_tbl) [1] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
[16] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
[31] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
[46] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUEIt detects the presence or absence of a pattern in a string.
str_order
The str_order(x) function returns a numeric vector that corresponds to the alphabetical order of the strings in the provided vector (x).
head(state.name)[1] "Alabama" "Alaska" "Arizona" "Arkansas" "California"
[6] "Colorado" str_order(state.name) [1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
[26] 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50head(state.abb)[1] "AL" "AK" "AZ" "AR" "CA" "CO"str_order(state.abb) [1] 2 1 4 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 15 12 13 14 16 17 18 21 20 19 22 23 25 24
[26] 26 33 34 27 29 30 31 28 32 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 46 45 47 49 48 50str_replace
The str_replace(string, pattern, replace) is equivalent to sub(pattern, replacement, x):
str_replace(string = state.name, pattern = "[Aa]", replace = "B") [1] "Blabama" "Blaska" "Brizona" "Brkansas"
[5] "CBlifornia" "ColorBdo" "Connecticut" "DelBware"
[9] "FloridB" "GeorgiB" "HBwaii" "IdBho"
[13] "Illinois" "IndiBna" "IowB" "KBnsas"
[17] "Kentucky" "LouisiBna" "MBine" "MBryland"
[21] "MBssachusetts" "MichigBn" "MinnesotB" "Mississippi"
[25] "Missouri" "MontBna" "NebrBska" "NevBda"
[29] "New HBmpshire" "New Jersey" "New Mexico" "New York"
[33] "North CBrolina" "North DBkota" "Ohio" "OklBhoma"
[37] "Oregon" "PennsylvBnia" "Rhode IslBnd" "South CBrolina"
[41] "South DBkota" "Tennessee" "TexBs" "UtBh"
[45] "Vermont" "VirginiB" "WBshington" "West VirginiB"
[49] "Wisconsin" "Wyoming" sub(pattern = "[Aa]", replacement = "B", x= state.name) [1] "Blabama" "Blaska" "Brizona" "Brkansas"
[5] "CBlifornia" "ColorBdo" "Connecticut" "DelBware"
[9] "FloridB" "GeorgiB" "HBwaii" "IdBho"
[13] "Illinois" "IndiBna" "IowB" "KBnsas"
[17] "Kentucky" "LouisiBna" "MBine" "MBryland"
[21] "MBssachusetts" "MichigBn" "MinnesotB" "Mississippi"
[25] "Missouri" "MontBna" "NebrBska" "NevBda"
[29] "New HBmpshire" "New Jersey" "New Mexico" "New York"
[33] "North CBrolina" "North DBkota" "Ohio" "OklBhoma"
[37] "Oregon" "PennsylvBnia" "Rhode IslBnd" "South CBrolina"
[41] "South DBkota" "Tennessee" "TexBs" "UtBh"
[45] "Vermont" "VirginiB" "WBshington" "West VirginiB"
[49] "Wisconsin" "Wyoming" str_pad
The str_pad(string, width, side, pad) function pads strings (string) with other characters, which is often useful when the string is going to be eventually printed for a person to read.
str_pad("Thai", width = 8, side = "left", pad = "-")[1] "----Thai"str_pad("Thai", width = 8, side = "right", pad = "-")[1] "Thai----"str_pad("Thai", width = 8, side = "both", pad = "-")[1] "--Thai--"The str_to_title(string) function acts just like tolower() and toupper() except it puts strings into Title Case.
cases <- c("CAPS", "low", "Title")
str_to_title(cases)[1] "Caps" "Low" "Title"str_trim
The str_trim(string) function deletes white space from both sides of a string.
to_trim <- c(" space", "the ", " final frontier ")
str_trim(to_trim)[1] "space" "the" "final frontier"str_wrap
The str_wrap(string) function inserts newlines in strings so that when the string is printed each line’s length is limited.
pasted_states <- paste(state.name[1:20], collapse = " ")
cat(str_wrap(pasted_states, width = 80))Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware Florida
Georgia Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine
Marylandcat(str_wrap(pasted_states, width = 30))Alabama Alaska Arizona
Arkansas California Colorado
Connecticut Delaware Florida
Georgia Hawaii Idaho Illinois
Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky
Louisiana Maine Marylandword
The word() function allows you to index each word in a string as if it were a vector.
a_tale <- "It was the best of times it was the worst of times it was the age of wisdom it was the age of foolishness"
word(a_tale, 2)[1] "was"word(a_tale, end = 3) # end = last word to extract[1] "It was the"word(a_tale, start = 11, end = 15) # start = first word to extract[1] "of times it was the"Post-lecture materials
Final Questions
Here are some post-lecture questions to help you think about the material discussed.
There is a corpus of common words here:
head(stringr::words)[1] "a" "able" "about" "absolute" "accept" "account" length(stringr::words)[1] 980- Using
stringr::words, create regular expressions that find all words that:
- Start with “y”.
- End with “x”
- Are exactly three letters long. (Don’t cheat by using str_length()!)
- Have seven letters or more.
- Using the same
stringr::words, create regular expressions to find all words that:
- Start with a vowel.
- That only contain consonants. (Hint: thinking about matching “not”-vowels.)
- End with
ed, but not witheed. - End with
ingorise.